Introduction
In Indian higher education, Turnitin is one of the most trusted plagiarism detection tools, used by both public and private universities. While most students and faculty know how to generate a plagiarism report, not everyone understands the difference between a Turnitin repository report and a private report. This lack of clarity often leads to unnecessary confusion, especially during the final submission of a thesis. For PhD candidates, this knowledge is not just technical—it is strategic. Choosing the right type of report can impact your similarity score and determine whether your work is accepted without objections.
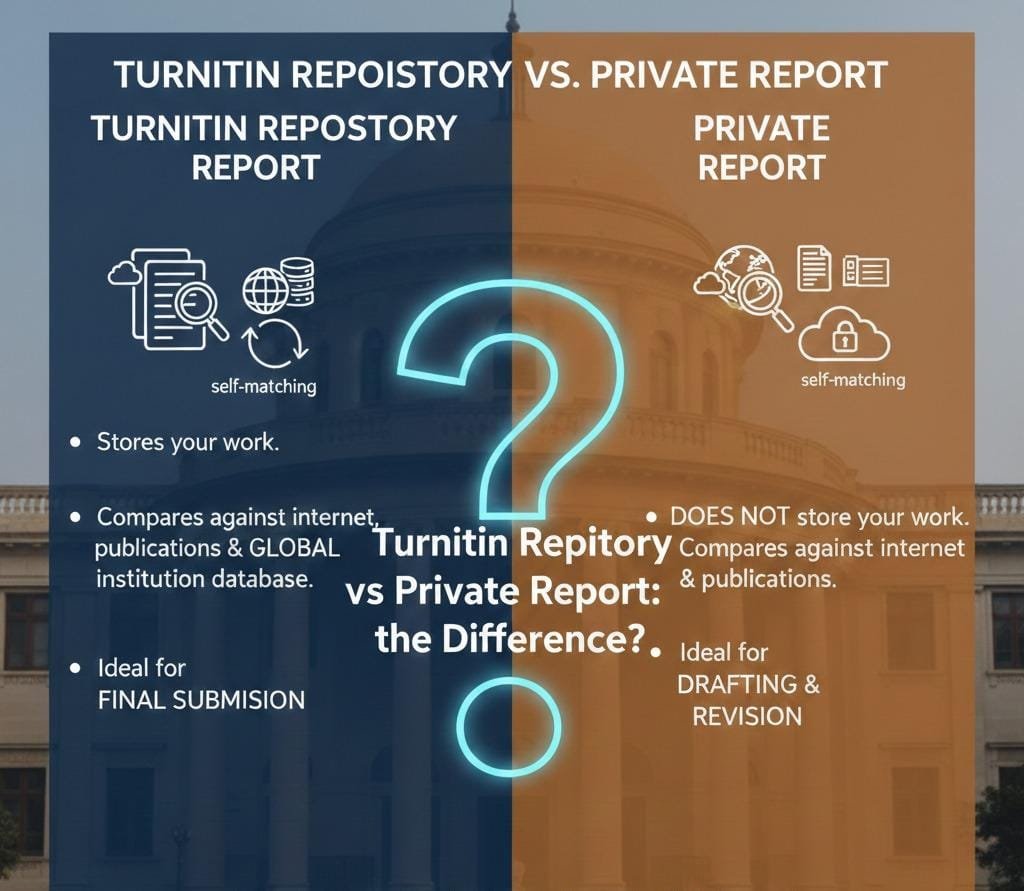
What Is the Turnitin Repository?
The Turnitin repository is a secure and vast database where academic work is stored after being checked. This includes student assignments, dissertations, theses, and research papers from institutions around the world. When a document is submitted for checking against the repository, Turnitin compares it not only with content available on the internet and in academic publications but also with all previously stored documents. This ensures a deep and thorough similarity check.
However, this can also cause a problem. If you have uploaded earlier drafts of your thesis to Turnitin through your university account, the system will detect similarities between your final version and those drafts. This is called “self-matching.” While self-matching is not plagiarism in the unethical sense, it still shows up in the similarity percentage. Many scholars panic when they see a high score without realising that the source is their own earlier work.
What Is a Private Report?
A private report in Turnitin is generated when your document is checked without being stored in the repository. The system still runs a comparison with online sources, subscription-based journals, and publications, but it does not store your document permanently. This method is useful for early checks because you can work on reducing similarity without worrying that each upload will be stored and compared in the future.
For example, if you are still refining your literature review and are concerned about accidental similarity, you can run it through a private check. This will highlight problem areas without affecting future repository comparisons.
When to Use a Private Report
Private reports are ideal during the drafting phase. They allow PhD students to identify problematic sections and make corrections before the official check. This is particularly helpful in private universities where thesis review timelines are strict, and even small delays can affect submission schedules. By running multiple private checks, you can gradually lower your similarity percentage before the final submission.
Faculty members also use private checks when guiding students through the writing process. It allows for safe monitoring of progress without compromising the originality score in the official submission stage.
When to Use a Repository Report
A repository report is best used for final submission or official evaluation. It ensures that the work has been checked against the widest possible range of sources, including previous submissions in the same institution. This makes it more reliable in terms of detecting any overlapping material that could be problematic.
However, you should only choose this option when you are confident that your work is as original as possible. If not, the repository check may flag earlier drafts or even sections from your own published articles, which could require further explanation to your review committee.
Benefits of Repository Reports
The main advantage of a repository check is its depth. By including stored documents in its comparison, Turnitin can identify similarities that a private check might miss. This is especially valuable for detecting recycled content from other students or from institutional archives. In the Indian PhD context, where academic scrutiny is increasing, such thoroughness can protect the scholar and the institution from future disputes.
Risks of Repository Reports
The main drawback is the potential for inflated similarity scores due to self-matching. While faculty members can differentiate between self-matching and actual plagiarism, it can still slow down the approval process. Some institutions require students to explain every similarity flagged, even if it comes from their own earlier work. This can add unnecessary administrative work in the final stages of the PhD.
Balancing the Two Approaches
For most PhD students in private universities, the most effective strategy is to use both types of reports at different stages. Start with private checks during the writing and revision process. This allows you to refine your content without adding it to the repository. Once you are confident in your work, run a final repository check for submission.
This balanced approach ensures you benefit from both flexibility and thoroughness. It also helps you avoid last-minute surprises that can delay your viva or final approval.
Common Misunderstandings
Many students believe that private reports are less “authentic” than repository reports. In reality, both use the same technology and search databases—except for the repository’s added stored documents. Another misconception is that a repository check will automatically detect plagiarism more effectively. While it is more comprehensive, a poorly written draft can still pass a repository check if it cleverly avoids direct overlaps but still uses unoriginal ideas without citation. This is why understanding plagiarism beyond just similarity percentage is essential.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Turnitin repository and private reports is not just a technical detail—it is an important part of academic strategy. For PhD students in private universities, using private reports during drafting and a final repository check before submission can save time, reduce stress, and prevent avoidable delays. By making informed choices, scholars can ensure their thesis meets originality requirements while navigating the complexities of plagiarism detection with confidence.
